In a Nutshell:
both sapphires and rubies belong to the Corundum family, meaning they share the same mineral composition but display a variety of colors. Essentially, sapphires encompass all the colors of corundum except for red, while rubies specifically denote the red varieties within the corundum spectrum.
A corundum is a mineral and a crystalline form of aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃). It is one of the hardest known minerals and is highly valued as a gemstone. Let’s explore in detail:
Chemical Composition:
- Corundum has a chemical formula of Al₂O₃, which means it is composed of aluminum and oxygen atoms. It is an oxide mineral.
Crystal Structure:
- The crystal structure of corundum is trigonal. The basic building blocks of the crystal structure are aluminum ions (Al³⁺) surrounded by oxygen ions (O²⁻) arranged in a hexagonal pattern. This crystal structure contributes to the mineral’s hardness and other physical properties.
Density:
- The density of corundum typically ranges from approximately 3.95 to 4.05 grams per cubic centimeter. This density is relatively high, contributing to the heaviness and solid feel of corundum.
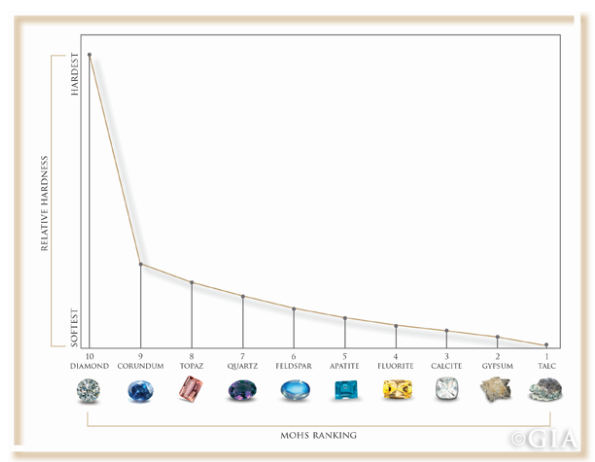
Mohs Scale Rating:
- Corundum is one of the hardest minerals on the Mohs scale, with a rating of 9. The Mohs scale measures the hardness of minerals on a scale from 1 (softest) to 10 (hardest). A rating of 9 indicates exceptional hardness, making corundum suitable for various industrial applications, including abrasive materials. Although please remember that the Mohs scale is basically an exponential scale, so the difference in hardness between a Diamond (10) and a Corundum (9) is much larger than the difference between the Corundum and the Topaz (8). For example a diamond is about 140 times harder than a corundum.
Please keep in mind that hardness is the resistance to scratch of a stone, not its resistance to breaks.
Refractive Index:
- The refractive index of corundum is relatively high, ranging from approximately 1.762 to 1.770. This high refractive index contributes to the brilliance and sparkle seen in gem-quality corundum, such as rubies and sapphires.
Varieties:
- Corundum occurs in a variety of colors. The red variety is known as ruby, while all other colors fall under the category of sapphire. The color variations are due to the presence of different trace elements. For example, chromium impurities give rubies their red color, while iron and titanium can impart various colors to sapphires.
Sapphires:
As mentioned quickly above Sapphires are Corundums that come is all colors excluding red, that includes dark pinks.
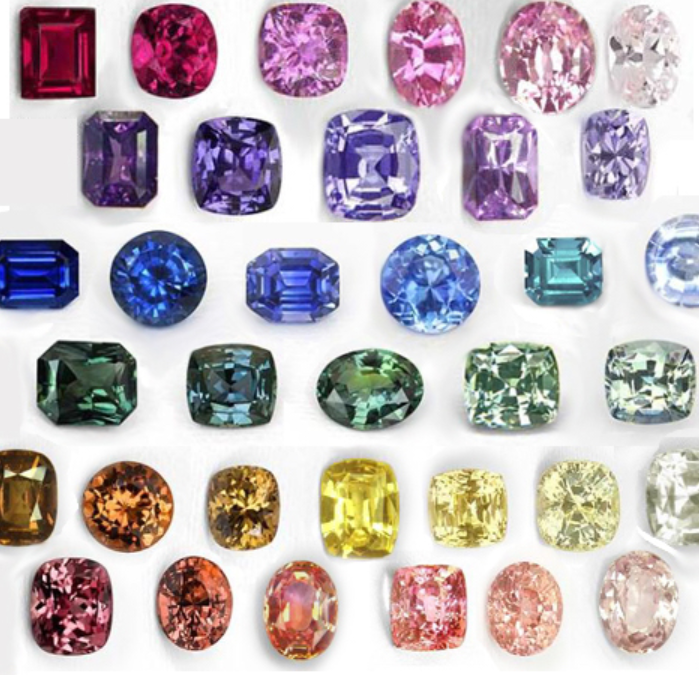

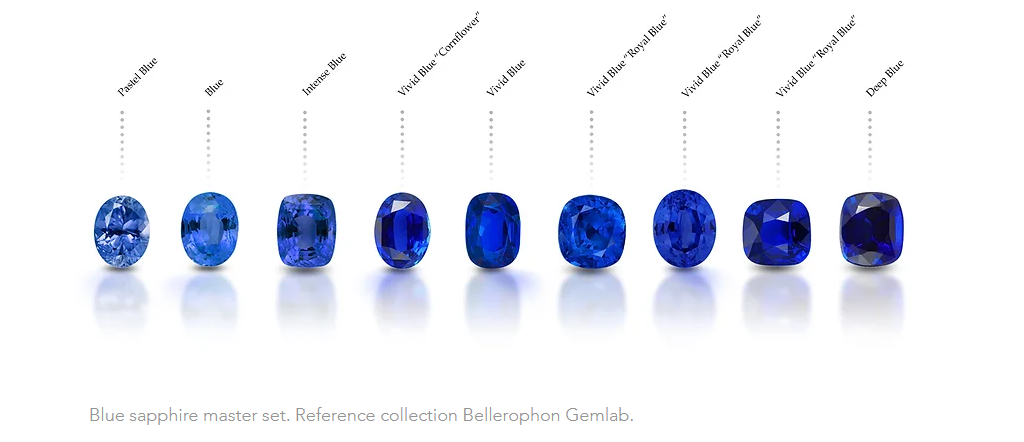
Sapphire hues aren’t just diverse; they’re also graded by their rarity and quality. Among these hues, some possess such exceptional rarity that they’ve earned their own distinctive names. Take, for instance, the Padparadscha, a captivating sapphire exhibiting a breathtaking sunset-like coloration (My personal favorite stone). Additionally, within the spectrum of blue sapphires, those esteemed for their superior saturation and hue are often referred to as Royal blue sapphires. These gems boast a mesmerizing deep blue-violet tone, symbolizing elegance and allure.

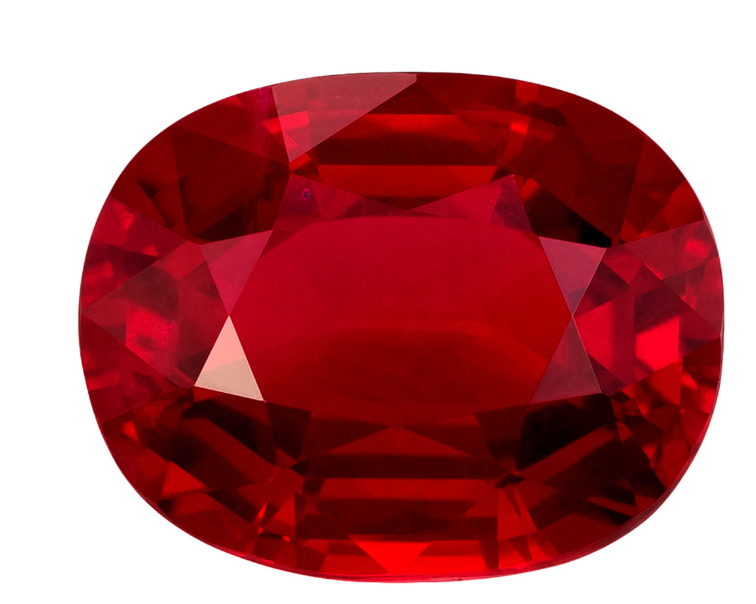
Rubies, are red Corundums, they encompass shades that exclude variations of pinks and oranges. Among them, the most esteemed red hue is often referred to as Pigeon Blood. This exquisite shade boasts a beautiful darker red tone, yet retains a subtle translucence, allowing light to pass through, enhancing its allure and brilliance.

Thank you for reading this post, I hope you have learned something new, if you have any question feel free to leave a comment and I will happily reply.
See you soon!






Pretty! This was a really wonderful article. Thanks for supplying this information.